Prefix Meaning Related To Computers
This week, the Global Cyber infinite Conference takes place in The Hague. In March, UNESCO hosted a conference on CONNECTing the Dots in Digital Space. The Net mundial Initiative had a meeting in Stanford recently. In early May, the Freedom Online Briefing volition accept place in Ulan Bator (for dates and a list of events come across the 2015 timeline).
In the Cyberspace field, prefix-switching (eastward-/net/cyber/digital) does non usually modify the meaning of the discussion or phrase. The Hague conference could have been called the Digital Space Conference; NETmundial could easily be CYBERmundial. Although these events take different prefixes, they deal with the same set of issues divers past the Un Committee on Science and Technology for Development equally ' international public policy bug pertaining to the Net'. They address all or some of 40+ issues that can exist classified in seven baskets, every bit illustrated in Diplo's 'IG Edifice Under Structure'.
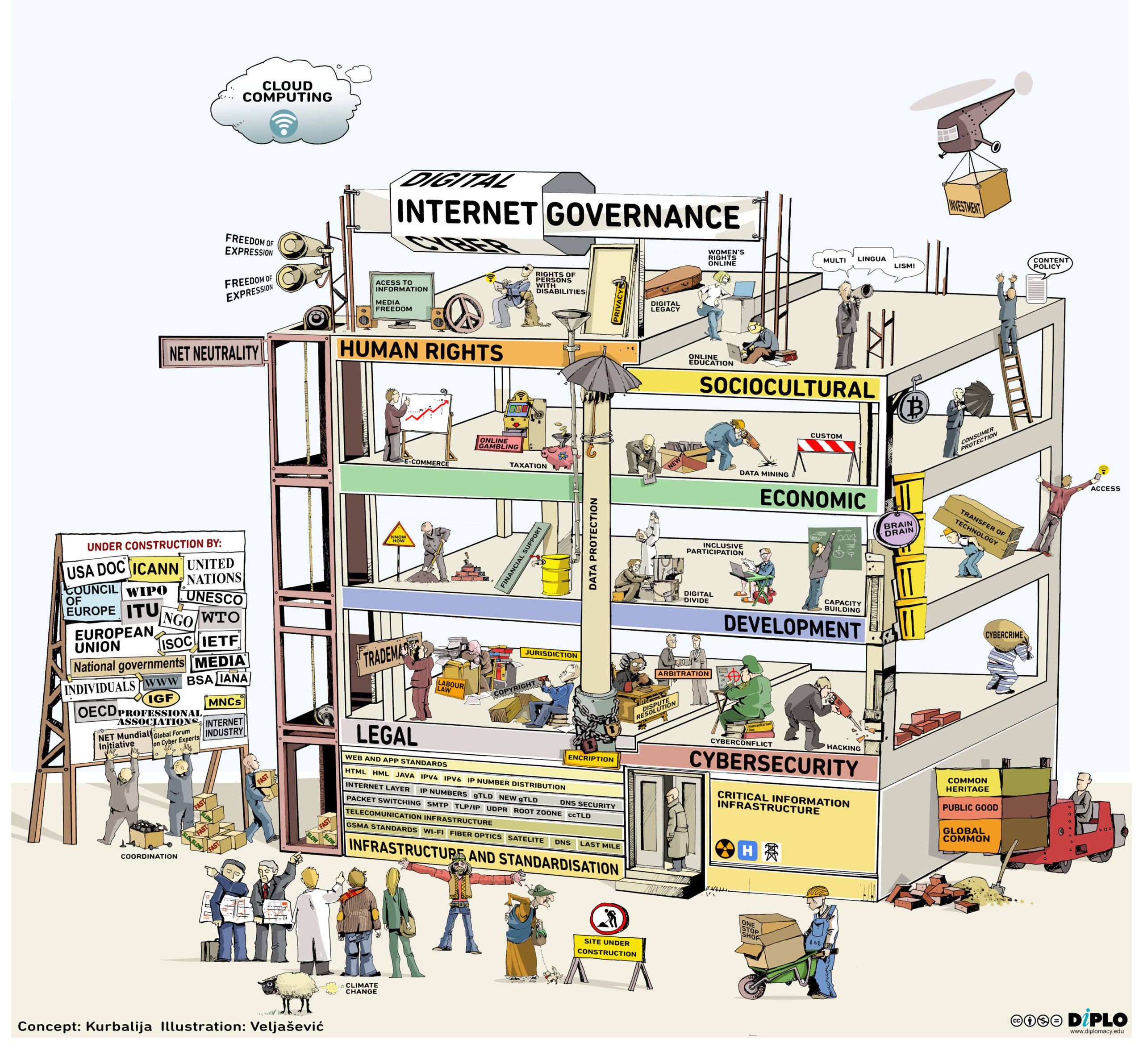
WHY DO PREFIXES MATTER, IF THEY CAN Be USED INTERCHANGEABLY?
Get-go , subtle trends in the use and implications of prefixes take started to sally. 'E-' is used typically for commerce, 'cyber' for security and crime, and 'digital' for evolution divides, to name a few. These trends are confirmed by a recent DiploFoundation written report analysing nine years of Internet Governance Forum (IGF) transcripts. For example, the written report shows a clear trend for the utilise of 'cyber' in give-and-take on security-related issues.
This process is non surprising. Each policy field tends to develop its own vocabulary, and to frame discussion in sure means. However, at that place is a potential risk if the unabridged Internet policy field comes to exist framed through one lens, such as security. For case, although the EU has the Digital Agenda as its core Net-related document, the EU Quango introduced the concept of cyber-diplomacy. Ane would accept expecteddigital diplomacy to exist a more appropriate proper name for a foreign diplomacy representation of the European union Digital Agenda.
In the USA ane can identify a wide range of prefixes. The e-Diplomacy unit of the US Country Department manages its Digital Diplomacy (utilise of the Internet in diplomatic activities) and runs, for instance, avirtual diplomatic mission to Iran. On the national level there is acybersecurity strategy. A similar 'prefix salad' can be found in many other countries worldwide.
Thesecond reason prefixes matter is that different prefixes could create defoliation for governments, companies and organisations that accept to deal with Internet public policy problems. Different prefixes may convey subtle – and mayhap wrong – implications near who should embrace unlike issues. During a recent lecture bout in Asia, I realised how hard is for governments to decide how to deal with these 'differences'. Who should be in charge of the various problems? Should it be the ministry for advice (digital) or security (cyber) or human rights (online) or…?
For small countries with express resources, this is becoming a existent problem. In a manner, by creating more possibilities to participate (more than events and more modes of participation), we risk of creating a 'paradox of inclusion' (more events, but fewer possibilities for small states to participate actively in about of them). The same claiming of managing the cyber/internet/virtual/e- barrage of events faces companies and the non-governmental sector.
Third , this procedure of covering similar issues under dissimilar titles may increase the difficulty of overcoming policy silos. Policy silos create sub-optimal coverage of multidisciplinary issues such as Internet governance. For instance, 1 cannot effectively accost cybersecurity without taking into consideration questions of privacy and freedom of expression, or business interests. Describing similar processes using different prefixes (cyber, digital, net,…) can accentuate the existing gap, making information technology even more complicated to bridge the policy silos.
WHAT CAN BE Done?
One has to be realistic in attempts to make policy-making rational. In spite of all efforts, policy-making is rarely optimal. It volition ever have an chemical element of irrationality, reflecting our imperfection as a gild. Security people will meet in their own circles, while human rights, technical communities, and others will tend to stay in their own spaces. Nosotros have to have this reality, merely we should not terminate our efforts to have multidisciplinary coverage of bug. In many cases nosotros will fail, but the efforts should be made. A few practical steps:
- Invest heavily in facilitation of communication among different policy communities (human rights, security, technology). It is not plenty to put different communities around a table and expect to have constructive advice. Creative and careful facilitation is required.
- Reduce the 'lost in translation' take a chance amid different professions by providing simple explanations of different concepts. Sometimes this will involve explanation of homographs such as 'protocol'. Protocol in diplomacy is not the same equally protocol in Internet technical advice (although both of them include 'handshaking').
- Create structural encouragements for communication among different professional groups. The IGF has been particularly successful in fostering multifariousness in the composition of discussion panels and other activities.
In essence, all of these prefixes (cyber, digital, net,..) refer to the same thing – the Internet. While the process of differentiating meanings and claiming terminology is a natural i, nosotros should be aware that we arecreating differences, rather thannaming differences which already exist.
Addendum – SHORT GUIDE FOR DIGITAL PREFIX ETYMOLOGY
The etymology of cyber goes back to the Ancient Greek meaning of 'governing'.Cyber came into utilize in our time via Norbert Weiner's book Cybernetics , dealing with information-driven governance. In 1984, William Gibson coined the discussionnet in the science fiction novel Neuromancer . The growth of the employ of the prefixcyber followed the growth of the Cyberspace. In the tardily 1990s, almost anything related to the Cyberspace was cyber: cyber community, cyber constabulary, cyber sex, cybercrime, cyber culture, cyber… Yous named anything on the Internet and you hadcyber. In the early 2000s,cyber gradually disappeared from broad apply, remaining alive principally in security terminology. One of the reasons is thatcyber was used in 2001 to proper noun the Quango of Europe Cybercrime Convention . It is still the merely international treaty in the field of Cyberspace security. Today we have, for example, the USA's Internet Strategy, the ITU's Global Cybersecurity Agenda ; NATO'due south cyber defence policy , and Estonia's Cyber Defense Centre of Excellence .
E – is the abbreviation for 'electronic'. It got its first and most important use througheastward-commerce, as description of early commercialisation of the Internet. Inthe EU's Lisbon Agenda (2000),e- was the most oftentimes used prefix.E– was also the master prefix in the declarations of the Earth Summit on the Data Social club (WSIS, Geneva 2003 and Tunis 2005). The WSIS follow-up implementation is centred on action lines includingeastward-government,e-business,eastward-learning,eastward-health,e-employment,due east-agronomics, ande-science. Nonetheless,due east– is non as nowadays every bit it used to be. Even the European union has abasede- recently, trying, virtually likely, to distance itself from the failure of the EU's Lisbon Agenda.
Today, the European union has a Digital Calendar for Europe . Digital refers to 'one' and '0' – two digits which are the ground of whole Internet earth. Ultimately, all software and programmes showtime with them. In the by,digital was used mainly in development circles to represent the digital divide. During the last few years,digital has started acquisition Internet linguistic space. In add-on to the European union, Great Britain now has digital diplomacy .
The prefix Internet almost disappeared afterwards initial popularity, in particular, in Frg (Netzpolitik). Information technology re-emerged with the growing importance of cyberspace neutrality discussion and last twelvemonth with NETmundial in Sao Paolo (Apr 2014). Hereafter of prefix Relevance of prefix Cyberspace will depend on the success of the N. a few years agone after Cyberspace was popular in early 2000s
Virtual relates to the intangible nature of the Internet.Virtual introduces the ambiguity of being both intangible and, potentially, non-existent.Virtualreality could be both an intangible reality (something that cannot be touched), and a reality that does non exist (false reality). Academics and Internet pioneers usedvirtual to highlight the novelty of the Internet, and the emergence of 'a brave new earth'.Virtual, considering of its cryptic significant, rarely appears in policy linguistic communication and international documents.
You can find more than information in the commodity 'Emerging Language of Internet Affairs'. Please let usa know if you would like to receive updates.
Dr Jovan Kurbalija is the director of DiploFoundtion and Head of the Geneva Internet Platform. You can contact him at jovank@affairs.edu
Prefix Meaning Related To Computers,
Source: https://www.diplomacy.edu/blog/different-prefixes-same-meaning-cyber-digital-net-online-virtual-e/#!
Posted by: taylorbeening.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Prefix Meaning Related To Computers"
Post a Comment